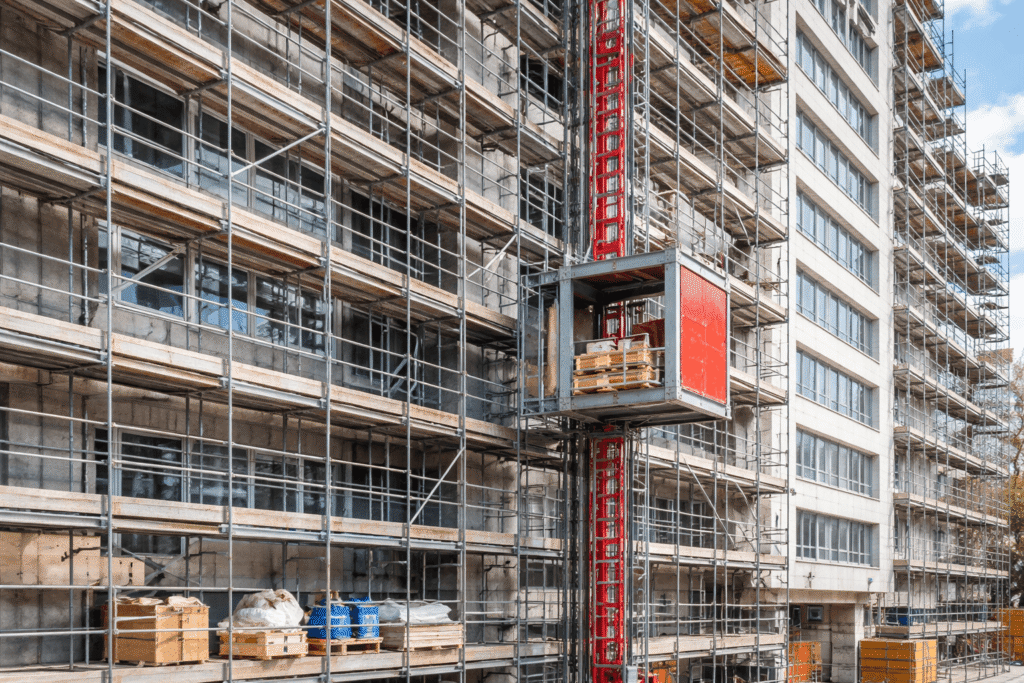
Facade construction relies on precise sequencing, steady material flow, and uninterrupted access to multiple elevations. Panels, glazing units, insulation, anchors, and tools must be delivered to scaffold platforms precisely when crews require them. When vertical transport slows, installers wait, scaffolding remains idle, and timelines begin to slip—often irreversibly on mid-rise and high-rise projects across Canada and the USA.
To prevent these issues, project teams must evaluate how materials are moved vertically. This comparison explains why material hoists for scaffolding outperform shared and temporary lifting options in demanding facade applications.
Vertical Transport Demands: Facade Work vs General Construction
Facade projects place far more repetitive and time-sensitive demands on vertical transport than many interior construction activities.
- Facade work requires frequent, predictable delivery of bulky components at changing elevations.
- General construction can often tolerate variability by staging materials indoors or adjusting sequencing.
Because scaffold platforms offer limited staging space, delays in material delivery immediately halt installation work. This makes the choice of vertical transport method a critical scheduling decision.
Material Hoists for Scaffolding vs Cranes
Cranes: Cranes are essential for structural lifting but are not optimized for repetitive facade-material handling.
- Shared across multiple trades
- Frequently reprioritized for structural or concrete work
- Irregular availability for facade crews
- Inefficient for repetitive, small-batch material delivery
Material Hoists for Scaffolding: Material hoists for scaffolding operate independently of crane schedules.
- Dedicated to facade material movement
- Fixed vertical paths aligned with scaffold elevations
- Consistent cycle times throughout the workday
- Predictable access for installers
Comparison outcome: Cranes are critical for major lifts, but material hoists for scaffolding provide the reliability needed to keep facade crews continuously productive.
Scaffolding Hoists vs Temporary Construction Lifts
Temporary Construction Lifts
Temporary lifts are often introduced as stopgap solutions.
- Limited speed and load capacity
- Not optimized for repetitive facade cycles
- Increased wait times during peak hours
- Often shared with personnel movement
Scaffolding Hoists
Scaffolding hoists are designed specifically to support exterior work.
- Faster vertical travel for repetitive loads
- Direct integration with scaffold systems
- Reduced queuing during peak installation periods
- Minimal interference with personnel movement
Comparison outcome: Scaffolding hoists deliver purpose-built performance, whereas temporary lifts struggle to meet facade production demands.
Material Hoists for Scaffolding vs Manual Handling
Manual Handling
Manual lifting is sometimes used for short distances or small components, but it quickly becomes a bottleneck.
- Slower material movement
- Increased safety risks
- High labor fatigue
- Inconsistent delivery timing
Material Hoists for Scaffolding
Material hoists eliminate inefficiencies associated with manual movement.
- Controlled vertical transport
- Reduced physical strain on crews
- Faster, repeatable cycles
- Improved safety and workflow consistency
Comparison outcome: Manual handling may appear flexible, but it introduces delays and risk, while material hoists for scaffolding support steady, safe progress.
Predictability and Scheduling Control
Shared Lifting Equipment
When facade crews depend on shared equipment, work sequencing becomes reactive.
- Crews wait for lift availability
- Material deliveries arrive out of order
- Installation zones experience uneven progress
Dedicated Scaffolding Hoists
Scaffolding hoists support proactive scheduling.
- Materials arrive when planned
- Crews maintain consistent output across elevations
- Sequencing remains aligned with facade installation plans
Comparison outcome: Dedicated hoists stabilize daily production and protect facade schedules from external disruptions.
Ground-Level Congestion: Hoists vs Staging Areas
Ground Staging
Relying on ground-level staging creates logistical pressure on constrained sites.
- Congested access routes
- Increased handling time
- Higher risk of material damage
Material Hoists for Scaffolding
Material hoists move components vertically instead of storing them at grade.
- Reduced ground congestion
- Clear access routes
- Safer, more organized site layout
Comparison outcome: Vertical delivery via scaffolding hoists improves both safety and efficiency on tight urban sites.
Performance Under High-Frequency Cycles
General-Purpose Lifting Solutions
Non-specialized equipment often struggles under continuous facade demand.
- Slower cycle times
- Increased downtime
- Wear-related interruptions
Material Hoists for Scaffolding
Material hoists designed for scaffold integration are designed to be durable.
- Rigid mast systems
- Guided platforms for load stability
- Controlled movement for frequent cycles
Comparison outcome: Material hoists for scaffolding sustain performance throughout high-frequency facade operations.
Impact on Labor Productivity and Costs
Inconsistent Vertical Transport
Unreliable access leads to:
- Idle installers
- Uneven facade progress
- Rising labor costs
Dedicated Scaffolding Hoists
Reliable hoisting systems help:
- Maximize productive labor hours
- Maintain even installation pacing
- Reduce indirect schedule-related costs
Comparison outcome: Investing in appropriate hoisting solutions directly protects labor efficiency.
Which Vertical Transport Method Best Supports Facade Projects?
When comparing vertical transport options, material hoists for scaffolding consistently deliver advantages that other methods cannot match. They provide speed, predictability, and dedicated access aligned with the unique demands of facade construction.
While cranes and temporary lifts play supporting roles, scaffolding hoists remain the most effective solution for maintaining momentum, reducing delays, and keeping facade projects on schedule across all elevations.